Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Case Report
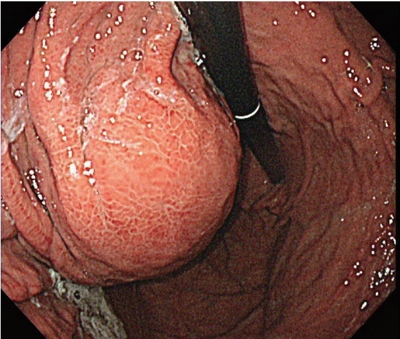
- Sorafenib-induced Pancreatic Pseudocyst in a Patient with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: a Rare Adverse Event
- Dae-ha Kim, Minkoo Kim, Hyung Joon Yim, Sang Jun Suh, Young Kul Jung
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):154-158. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.154
- 3,467 Views
- 47 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 54-year old man diagnosed with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma began treatment with sorafenib. After 3 weeks of treatment, he complained of abdominal pain and nausea. Abdominal sonography showed multiple hepatic lesions only. Serum amylase and lipase levels were 35 U/L and 191 U/L, respectively. The patient was diagnosed with sorafenib-induced acute pancreatitis. After 10 days of discontinuing sorafenib he still complained of nausea and loss of appetite. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy showed a large bulging lesion, which was suspected to cause extrinsic compression on the high body of the gastric anterior wall. Computed tomography scan revealed a cystic lesion, 8.3 cm in size, in the pancreatic tail, suggesting a pancreatic pseudocyst. After the withdrawal of sorafenib, systemic chemotherapy with Adriamycin and cisplatin was administered. Four months after the discontinuation of sorafenib, the size of the pancreatic pseudocyst decreased from 8.3 cm to 3 cm. The patient's symptoms were also relieved.

Original Article
- Factors Affecting Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis: Implications for Future Therapeutic Strategies
- Sang Jun Suh, Hyung Joon Yim, Dong Won Lee, Jong Jin Hyun, Young Kul Jung, Ji Hoon Kim, Yeon Seok Seo, Jong Eun Yeon, Kwan Soo Byun, Soon Ho Um
- J Liver Cancer. 2017;17(1):60-71. Published online March 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.17.1.60
- 2,136 Views
- 23 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
s: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT) exhibits poor prognosis. The aim of this study is to evaluate factors associated with survival of HCC patients with PVTT to suggest better therapeutic options.
Methods
Patients with HCC which were newly diagnosed at three tertiary hospitals between January 2004 and December 2012, were reviewed retrospectively. Among them, Barcelona Clinic of Liver Cancer stage C patients with PVTT were identified. Factors affecting overall survival (OS) were analyzed and efficacies of the treatment modalities were compared.
Results
Four hundred sixty five patients with HCC and PVTT were included. Liver function, tumor burden, presence of extrahepatic tumor, alfa fetoprotein, and treatment modalities were significant factors associated with OS. Treatment outcomes were different according to the initial modalities. OS of the patients who received hepatic resection, radiofrequency ablation (RFA), transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC), sorafenib, systemic cytotoxic chemotherapy, radiation therapy (without combination), and supportive care were 27.8, 7.1, 6.7, 5.3, 2.5, 3.0, 1.8, and 0.9 months, respectively (P<0.001). Curative-intent treatments such as hepatic resection or RFA were superior to noncurativeintent treatments (P<0.001). TACE or HAIC was superior to sorafenib or systemic chemotherapy (P<0.001). Combining radiotherapy to TACE or HAIC did not provide additional benefit on OS (P=0.096).
Conclusions
Treatment modalities as well as baseline factors significantly influenced on OS of HCC patients with PVTT. Whenever possible, curative intent treatments should be preferentially considered. If unable, locoregional therapy would be a better choice than systemic therapy in HCC patients with PVTT. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Value of surgical resection compared to transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A meta-analysis of hazard ratios from five observational studies
Keera Kang, Sung Kyu Song, Chul-Woon Chung, Yongkeun Park
Annals of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery.2020; 24(3): 243. CrossRef
- Value of surgical resection compared to transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A meta-analysis of hazard ratios from five observational studies

Case Reports
- A Case of Successful Hepatic Resection after Insufficient Response to Transarterial Chemoembolization and Radiation Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Invasion
- Seong Kyun Na, Hyung Joon Yim, Sang Jun Suh, Young Kul Jung
- J Liver Cancer. 2016;16(2):118-122. Published online September 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.16.2.118
- 932 Views
- 5 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with portal vein invasion has a poor prognosis. Treatments such as transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), radiation therapy (RT), sorafenib are done as a first line treatment. But in case of incomplete response to first line treatment, there’s no established guideline about salvage treatment. We present a 47 year-old male who was diagnosed as HCC with portal vein invasion. He was treated with RT and repeated TACE, but remnant viable tumor was observed. Surgical resection was performed as a salvage treatment, and HCC was completely removed. He has been followed up over 3 years, but there was no recurrence.

- A Case Report of Transarterial Chemoembolization and Stereotactic Radiation Therapy before Liver Transplantation in a Decompensated Cirrhosis with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Sang Hoon Kim, Joo Hee Park, Sang Jun Suh, Young Kul Jung, Hyung Joon Yim
- J Liver Cancer. 2014;14(2):135-138. Published online September 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.14.2.135
- 952 Views
- 4 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Liver transplantation is the only curable treatment modality for hepatocellular carcinoma with advanced liver cirrhosis. While treatment outcome of the liver transplantation is improving, time needed to standby until the surgery is getting longer because of both the lack of liver donors and increasing demands for the transplantation. Therefore, importance of bridging therapy before the liver transplantation is recently highlighted. We herein report our recent experience about a patient who successfully undergone transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and stereotactic radiation therapy (START) as bridging therapy and later had liver transplantation operation. (J Liver Cancer 2014;14:135-138)


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter